The Mughal Empire
Art

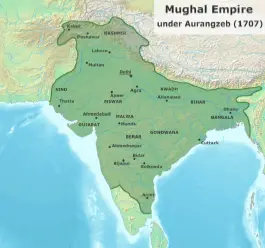
The Mughal Empire
There are many different cultures in India. Religions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, and Jainism are all embedded throughout the cultural landscape of India. Additionally, India has a cultural history with Islam, which was embedded in the culture of the Mughals. But what is Mughal? The Mughal Empire was an early but modern Islamic empire that dominated South Asia and the Indian subcontinent from 1526 until its dissolution in 1857.
The empire grew out of a sustained military campaign that established a new government and administration.
The Mughal Empire was established in 1526 by the warrior chieftain of Andijan, Babur, who defeated the Sultan of Delhi, Ibrahim Lodhi, and then the Rajputs and Afghans before expanding down into the plains of upper India.
The capital of the Mughal Empire had been multiple cities such as Agra, Kabul, Fatehpur Sikri, Delhi, and Lahore. The common languages of the people who lived under the Mughal Empire include Urdu, the language of the ruling class; Hindavi Arabic for religious ceremonies; Persian was used as the court language; Chagatai Turkic was used for a short time, as were many other South Asian languages.
The Mughals also claimed ancestry that is both Turkish and Mongolian, with connections to the Arabian Peninsula.
The religions of the Mughal Empire, therefore, included the Hanafi school of Sunni Islam, in addition to a religion called Din-i-Ilahi or “Oneness of God”. The latter was a syncretic religion that the Mughal emperor Akbar (1556-1605) attempted to draw from, and he merged aspects primarily from Islam, Hinduism, and Zoroastrianism, but also Christianity, Buddhism, and Jainism.
Scattered throughout India are the remnants of the Mughal Empire. Many of these architectural remnants are among the UNESCO World Heritage Sites. And many of its literary forms, textiles, and paintings, which were the belongings and consumptions of the Mughal elite, remain and are housed in museums.
Mughal Empire Art
The Mughal Empire became so prominent and prosperous that it became a significant contributor to the arts; it took much of its influences from Indo-Persian-Islamic content, context, symbolism, aesthetics, meaning, and narrative.
The main features of Mughal art are recognized in the aesthetics which are influenced by Persian, Indian, and Islamic styles. Mughal art often uses geometric shapes, detailed ornamentation, vibrant colors, and even gold.
Mughal art developed throughout the reigns of several rulers who encouraged and bolstered the prosperity of culture, art and architecture, which to them expressed refinement and benevolence. Such rulers included:
- Babur (1526-1530) –
- Humayun (1530-1556)
- Muhammad Akbar (1556-1605)
- Jahangir (1605-1627)
- Shah Jahan (1628-1658)
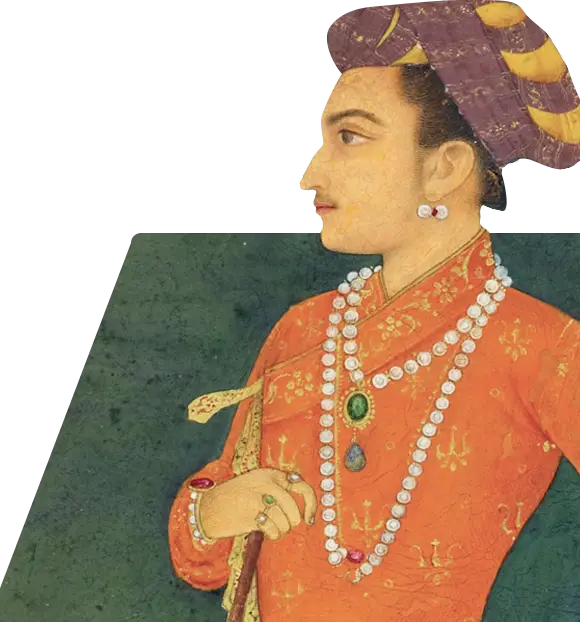
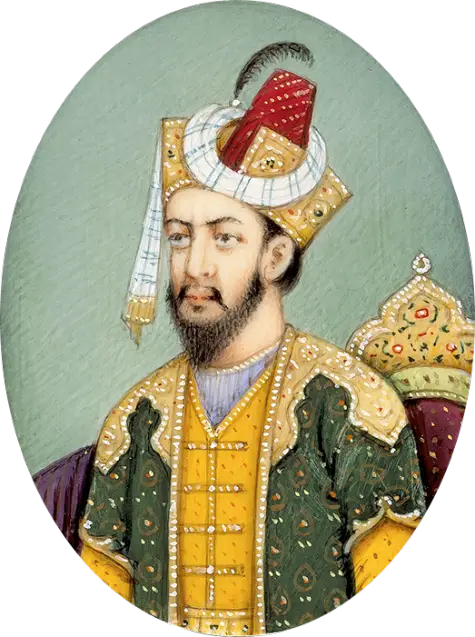


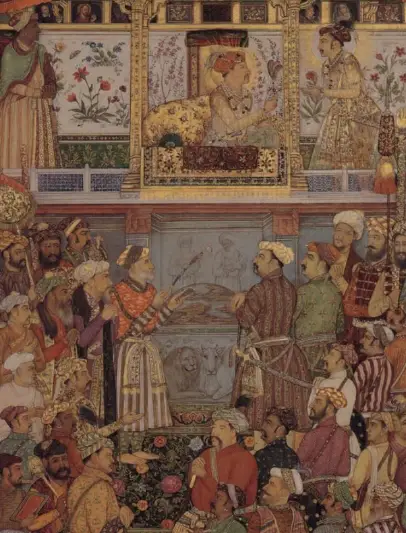
Mughal Empire art became an expression of refinement and benevolence for Mughal emperors. They commissioned large projects for creating illustrated books depicting important historical events and scenes, and documenting aspects of government and court life. Art would later branch off to single images and portraits of elite and serene lifestyles, luxury objects, and the tranquility and beauty of the natural world.
Mughal painting developed out of Persian and Islamic style influences that Emperor Humayun was exposed to and promoted in his court. Humayun specifically brought artists to India in order to commission them in helping develop a Mughal Empire style of painting or Mughal aesthetic.
The Mughal artistic tradition became mainly expressed in painted miniatures or small portraits or paintings that could fit inside books as their illustrations. Miniature paintings usually accompanied some work of philosophy, poetry, history, or religious scripture. The paintings used vibrant colors originally inspired by Persian works to depict the eccentric and vibrant clothes of subjects. The color schemes later evolved to mimic the various color palette throughout other aspects of Indian culture and biodiversity.
The Mughal Empire is also known for its architecture as well as paintings. The architecture of Mughal is easily recognized by its detailed ornamentation, and use of symmetry and geometry. Additionally, much of the architecture is made of red sandstone, but sometimes marble is used instead. The architecture also uses many arches and sometimes soft and curvy structures like those under Shah Jahan.
The most famous piece of architecture of the Mughal Empire is the Taj Mahal commissioned under Shah Jahan.Such works are in contrast to the more rigid structures created by Emperor Akbar, such as much of the construction in the city of Fatehpur Sikri.
Mughal art and architecture continue to deeply influence Indian culture, art and design. The Mughal design has many variations, including Mughal inspired Art Déco design such as the Umaid Bhawan Palace in Jodhpur.